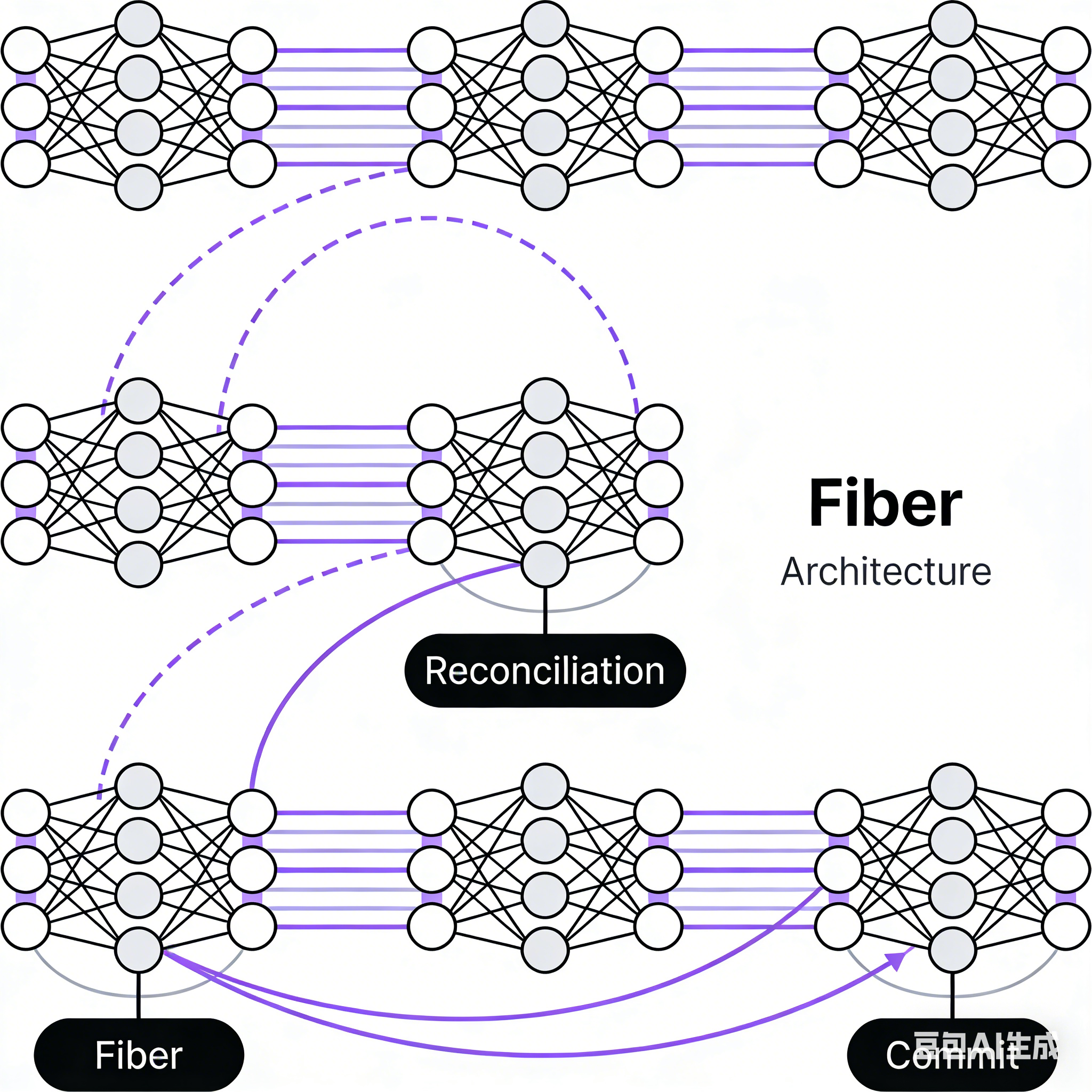
Fiber架构的背景
传统Stack Reconciler的局限性
在Fiber架构之前,React使用Stack Reconciler(栈协调器),存在以下问题:
- 不可中断的渲染:一旦开始渲染,必须完成整个树的计算
- 阻塞主线程:大量计算会导致页面卡顿
- 优先级处理困难:无法区分高优先级和低优先级更新
Fiber架构的设计目标
- 可中断的工作:将渲染工作分解为小单元,可以暂停和恢复
- 优先级调度:根据不同优先级安排工作执行顺序
- 并发渲染:支持并发模式下的渲染
- 错误边界:更好的错误处理机制
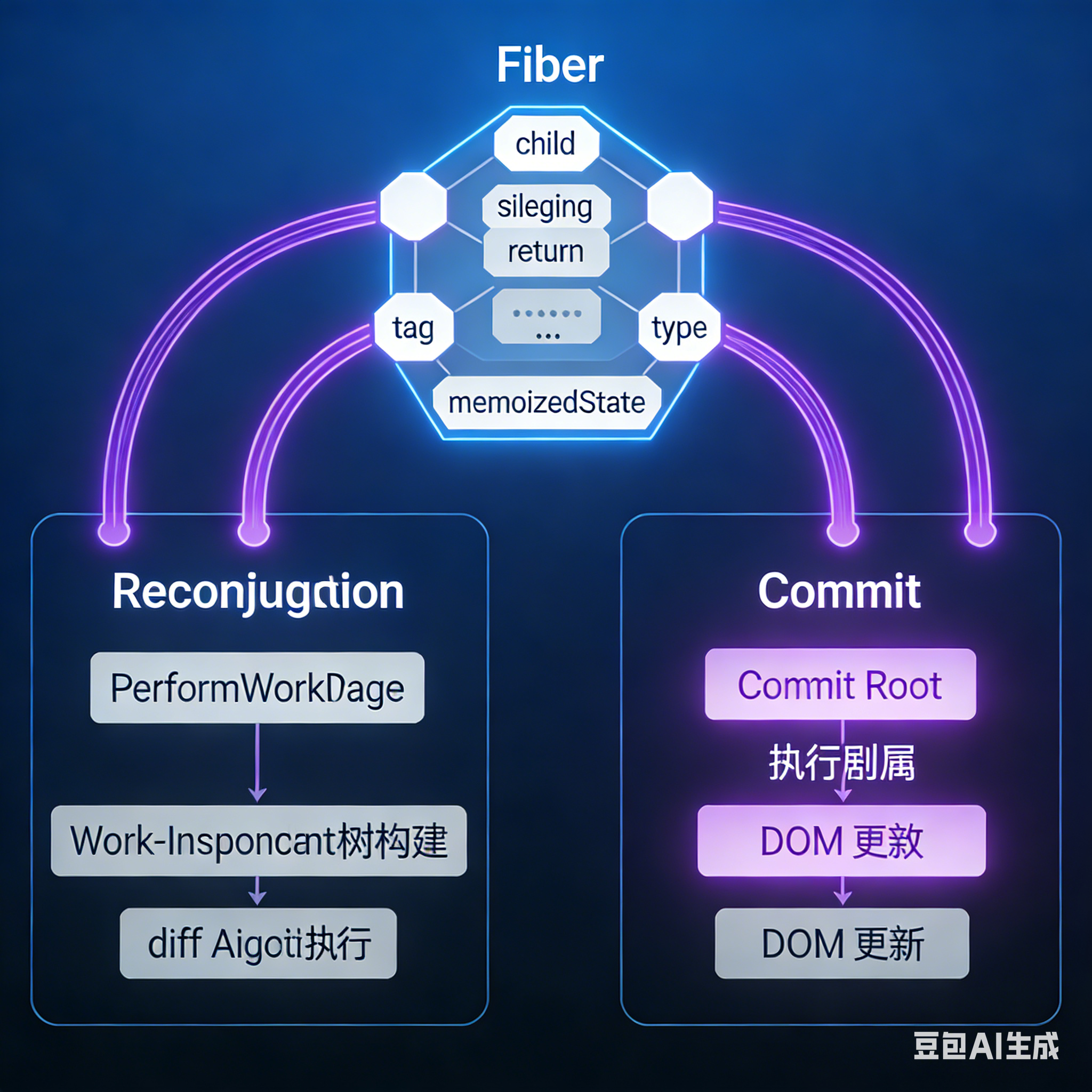
Fiber节点的数据结构
Fiber节点的核心属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
const fiberNode = {
tag: WorkTag,
key: null,
type: null,
stateNode: null,
memoizedProps: null,
memoizedState: null,
updateQueue: null,
return: null,
child: null,
sibling: null,
index: 0,
flags: 0,
subtreeFlags: 0,
deletions: null,
alternate: null,
lanes: 0,
childLanes: 0,
mode: 0,
};
|
Fiber树的链表结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
const fiberTree = {
tag: FunctionComponent,
type: App,
child: {
tag: FunctionComponent,
type: Header,
return: AppFiber,
sibling: {
tag: FunctionComponent,
type: Content,
return: AppFiber,
child: {
tag: HostComponent,
type: 'p',
return: ContentFiber
},
sibling: null
}
}
};
|
Fiber架构的工作流程
双缓存技术(Double Buffering)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
let current = null;
let workInProgress = null;
function prepareFreshStack(root) {
workInProgress = createWorkInProgress(current, null);
}
function commitRoot() {
const finishedWork = workInProgress;
current = finishedWork;
workInProgress = null;
}
|
工作循环(Work Loop)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| function workLoop(deadline) {
let shouldYield = false;
while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYield) {
nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork);
shouldYield = deadline.timeRemaining() < 1;
}
if (nextUnitOfWork !== null) {
requestIdleCallback(workLoop);
} else {
commitRoot();
}
}
|
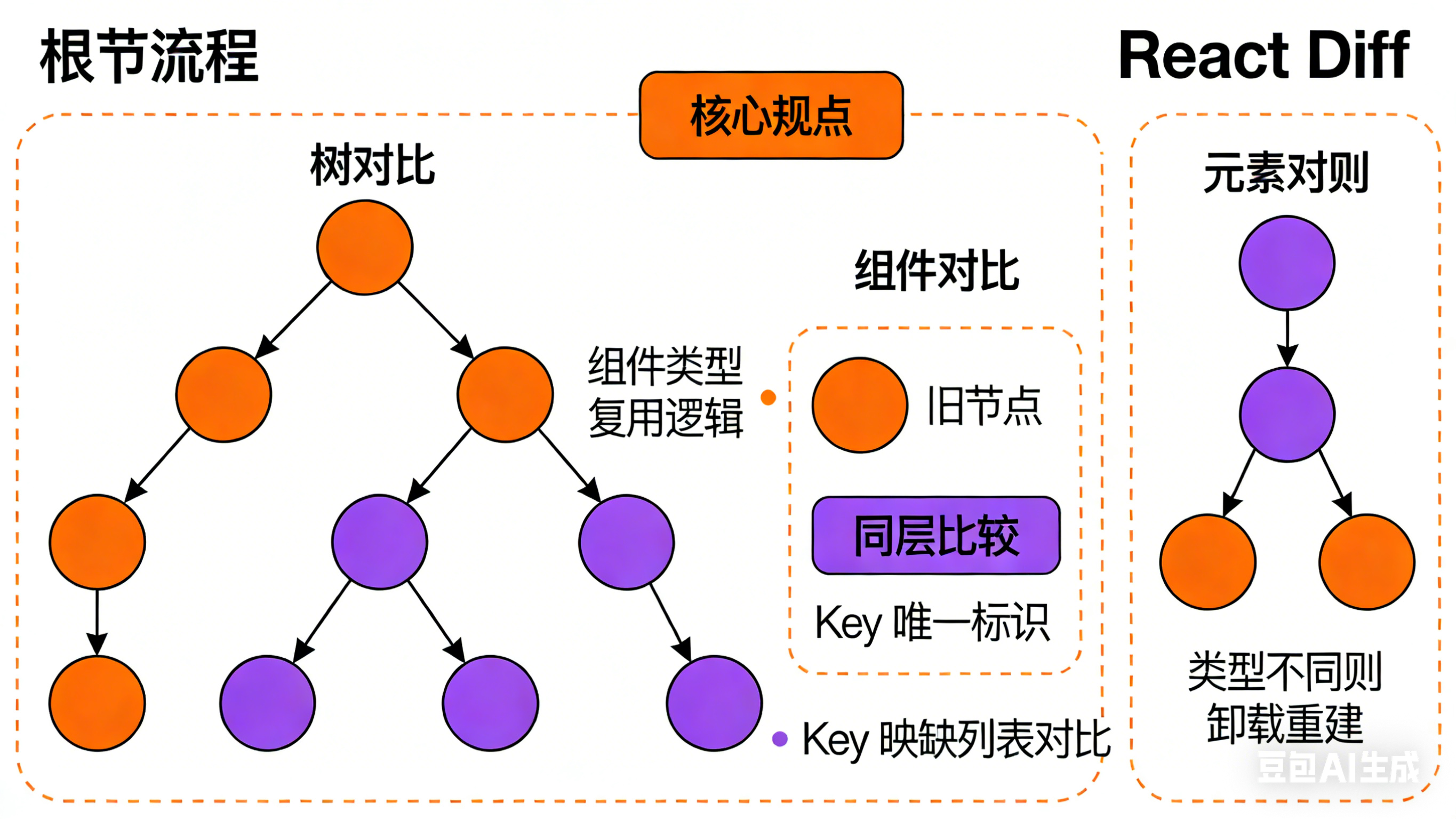
协调算法(Reconciliation)
Diff算法优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| function reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChildren,
lanes
) {
let resultingFirstChild = null;
let previousNewFiber = null;
let oldFiber = currentFirstChild;
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;
let newIdx = 0;
let nextOldFiber = null;
for (; oldFiber !== null && newIdx < newChildren.length; newIdx++) {
if (oldFiber.index > newIdx) {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber;
oldFiber = null;
} else {
nextOldFiber = oldFiber.sibling;
}
const newFiber = updateSlot(
returnFiber,
oldFiber,
newChildren[newIdx],
lanes
);
if (newFiber === null) {
if (oldFiber === null) {
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
break;
}
lastPlacedIndex = placeChild(newFiber, lastPlacedIndex, newIdx);
if (previousNewFiber === null) {
resultingFirstChild = newFiber;
} else {
previousNewFiber.sibling = newFiber;
}
previousNewFiber = newFiber;
oldFiber = nextOldFiber;
}
}
|
优先级调度(Lane模型)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
export const NoLanes = 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const NoLane = 0b0000000000000000000000000000000;
export const SyncLane = 0b0000000000000000000000000000001;
export const InputContinuousLane = 0b0000000000000000000000000000010;
export const DefaultLane = 0b0000000000000000000000000000100;
export const IdleLane = 0b0100000000000000000000000000000;
export const OffscreenLane = 0b1000000000000000000000000000000;
function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane) {
markRootUpdated(root, lane);
if (lane === SyncLane) {
performSyncWorkOnRoot(root);
} else {
ensureRootIsScheduled(root);
}
}
|
并发模式(Concurrent Mode)
可中断渲染
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root) {
if (shouldYield()) {
return null;
}
const didFullyRender = renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes);
if (didFullyRender) {
const finishedWork = root.current.alternate;
commitRoot(root, finishedWork);
}
return null;
}
|
Suspense和懒加载
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| function lazy(ctor) {
let thenable = null;
return {
$$typeof: REACT_LAZY_TYPE,
_payload: {
_status: -1,
_result: ctor,
},
_init(payload) {
if (payload._status === -1) {
const ctor = payload._result;
thenable = ctor();
payload._status = 0;
payload._result = thenable;
}
switch (payload._status) {
case 0:
throw thenable;
case 1:
return payload._result;
case 2:
throw payload._result;
}
}
};
}
|
错误处理机制
Error Boundaries的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { hasError: false };
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
return { hasError: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
logErrorToService(error, errorInfo);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasError) {
return this.props.fallback;
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
|
Fiber架构中的错误处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| function throwException(
root,
returnFiber,
sourceFiber,
value,
rootRenderLanes
) {
sourceFiber.flags |= Incomplete;
if (
value !== null &&
typeof value === 'object' &&
typeof value.then === 'function'
) {
} else {
let workInProgress = returnFiber;
do {
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case ClassComponent:
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
if (
typeof instance.componentDidCatch === 'function' &&
!isAlreadyFailedLegacyErrorBoundary(instance)
) {
const lane = requestUpdateLane();
const update = createClassErrorUpdate(
workInProgress,
value,
lane
);
enqueueUpdate(workInProgress, update, lane);
markRootUpdated(root, lane);
return;
}
break;
case HostRoot:
break;
}
workInProgress = workInProgress.return;
} while (workInProgress !== null);
}
}
|
性能优化策略
时间分片(Time Slicing)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| function shouldYield() {
return (
deadline !== null &&
deadline.timeRemaining() <= 0 &&
(needsPaint || scheduler.shouldYieldToHost())
);
}
|
优先级标记(Priority Marking)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| function markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(sourceFiber, lane) {
sourceFiber.lanes |= lane;
let node = sourceFiber;
let parent = sourceFiber.return;
while (parent !== null) {
parent.childLanes |= lane;
node = parent;
parent = parent.return;
}
if (node.tag === HostRoot) {
return node.stateNode;
}
return null;
}
|
调试和开发工具
Fiber树的调试信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
function getFiberDescription(fiber) {
return {
tag: getTagName(fiber.tag),
type: fiber.type ? fiber.type.name || fiber.type : null,
key: fiber.key,
state: fiber.memoizedState,
props: fiber.memoizedProps,
lanes: formatLanes(fiber.lanes),
childLanes: formatLanes(fiber.childLanes)
};
}
|
实战:简易Fiber实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
class MiniFiber {
constructor(type, props) {
this.type = type;
this.props = props;
this.dom = null;
this.child = null;
this.sibling = null;
this.return = null;
this.alternate = null;
this.effectTag = null;
}
}
function createElement(type, props, ...children) {
return {
type,
props: {
...props,
children: children.map(child =>
typeof child === 'object' ? child : createTextElement(child)
)
}
};
}
function createTextElement(text) {
return {
type: 'TEXT_ELEMENT',
props: {
nodeValue: text,
children: []
}
};
}
|
Fiber架构的未来发展
并发特性的扩展
- useTransition:管理并发更新的过渡状态
- useDeferredValue:延迟某些值的更新
- Offscreen:预渲染和缓存组件
服务器组件(Server Components)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
async function ServerComponent() {
const data = await fetchData();
return <div>{data}</div>;
}
function ClientComponent() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<ServerComponent />
</Suspense>
);
}
|
总结
React Fiber架构通过重新设计协调算法和引入并发概念,解决了传统架构的性能瓶颈。Fiber的核心思想是将渲染工作分解为可中断的小单元,支持优先级调度和并发渲染。