Diff算法的核心挑战
传统树比较的复杂度问题
传统的树比较算法(如Tree Edit Distance)时间复杂度为O(n³),其中n是树的节点数量。对于大型应用来说,这种复杂度是完全不可接受的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
function treeEditDistance(tree1, tree2) {
}
|
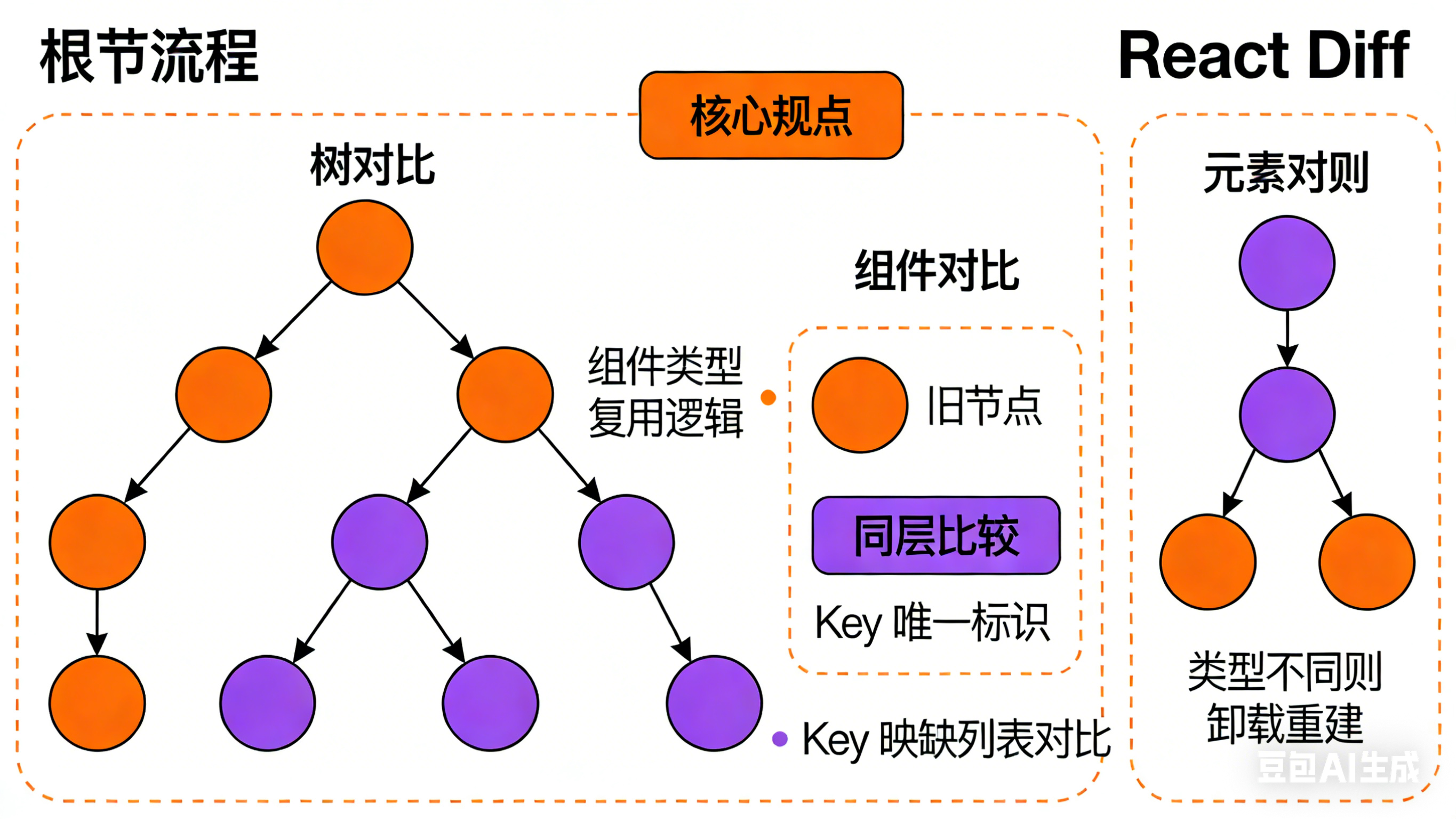
React的优化策略
React通过以下启发式规则将复杂度降低到O(n):
- 类型不同则完全替换:如果元素类型不同,直接替换整个子树
- 键值标识元素:通过key属性识别元素的移动和复用
- 同级比较:只在同级元素间进行比较,不跨层级
Diff算法的三层比较策略
1. 树层级比较(Tree Level)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| function diffTrees(oldTree, newTree) {
if (oldTree.type !== newTree.type) {
return { type: 'REPLACE', newTree };
}
const propPatches = diffProps(oldTree.props, newTree.props);
const childPatches = diffChildren(
oldTree.props.children,
newTree.props.children
);
return { type: 'UPDATE', propPatches, childPatches };
}
|
2. 组件层级比较(Component Level)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| function shouldUpdateComponent(prevElement, nextElement) {
if (prevElement.type !== nextElement.type) {
return true;
}
if (prevElement.key !== nextElement.key) {
return true;
}
return !shallowEqual(prevElement.props, nextElement.props);
}
|
3. 元素层级比较(Element Level)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| function diffChildren(oldChildren, newChildren) {
const patches = [];
const oldMap = createKeyToOldIdxMap(oldChildren);
let newIdx = 0;
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;
while (newIdx < newChildren.length) {
const newChild = newChildren[newIdx];
const oldIdx = oldMap[newChild.key];
if (oldIdx === undefined) {
patches.push(createInsertPatch(newChild, newIdx));
} else {
const oldChild = oldChildren[oldIdx];
if (shouldUpdateElement(oldChild, newChild)) {
patches.push(createUpdatePatch(oldChild, newChild, newIdx));
}
if (oldIdx < lastPlacedIndex) {
patches.push(createMovePatch(newChild, newIdx));
}
lastPlacedIndex = Math.max(oldIdx, lastPlacedIndex);
}
newIdx++;
}
return patches;
}
|
Key的重要性和实现原理
Key的作用机制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| function createKeyToOldIdxMap(children) {
const map = {};
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
const child = children[i];
if (child.key != null) {
if (map[child.key] !== undefined) {
console.warn('Duplicate keys detected:', child.key);
}
map[child.key] = i;
}
}
return map;
}
|
Key的最佳实践
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
const badList = items.map((item, index) => (
<Item key={index} item={item} />
));
const goodList = items.map(item => (
<Item key={item.id} item={item} />
));
const staticList = staticItems.map((item, index) => (
<Item key={index} item={item} />
));
|
列表Diff的详细算法
最长递增子序列(LIS)优化
React使用最长递增子序列算法来最小化DOM操作:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| function findLongestIncreasingSubsequence(arr) {
const piles = [];
const sequence = [];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const num = arr[i];
let left = 0;
let right = piles.length;
while (left < right) {
const mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
if (piles[mid] < num) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
if (left < piles.length) {
piles[left] = num;
} else {
piles.push(num);
}
sequence[i] = left > 0 ? sequence[left - 1] : -1;
}
const lis = [];
let current = piles.length - 1;
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (sequence[i] === current) {
lis.unshift(arr[i]);
current--;
}
}
return lis;
}
|
移动检测算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| function calculateMoves(oldIndices, newIndices) {
const moves = [];
const source = oldIndices.slice();
const dest = newIndices.slice();
const lis = findLongestIncreasingSubsequence(dest);
const shouldMove = new Array(dest.length).fill(true);
for (const index of lis) {
shouldMove[index] = false;
}
for (let i = dest.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (shouldMove[i]) {
moves.push({
type: 'MOVE',
from: source.indexOf(dest[i]),
to: i
});
}
}
return moves;
}
|
Fiber架构中的Diff实现
双缓存技术的Diff
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| function reconcileChildFibers(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChildren,
lanes
) {
if (typeof newChildren === 'object' && newChildren !== null) {
switch (newChildren.$$typeof) {
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChildren,
lanes
)
);
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSinglePortal(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChildren,
lanes
)
);
default:
if (isArray(newChildren)) {
return reconcileChildrenArray(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
newChildren,
lanes
);
}
}
}
if (typeof newChildren === 'string' || typeof newChildren === 'number') {
return placeSingleChild(
reconcileSingleTextNode(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
'' + newChildren,
lanes
)
);
}
return deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, currentFirstChild);
}
|
单元素Diff
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| function reconcileSingleElement(
returnFiber,
currentFirstChild,
element,
lanes
) {
const key = element.key;
let child = currentFirstChild;
while (child !== null) {
if (child.key === key) {
if (child.type === element.type) {
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, child.sibling);
const existing = useFiber(child, element.props);
existing.return = returnFiber;
return existing;
} else {
deleteRemainingChildren(returnFiber, child);
break;
}
} else {
deleteChild(returnFiber, child);
}
child = child.sibling;
}
const created = createFiberFromElement(element, returnFiber.mode, lanes);
created.return = returnFiber;
return created;
}
|
性能优化策略
shouldComponentUpdate的优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class OptimizedComponent extends React.Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return !shallowEqual(this.props, nextProps) ||
!shallowEqual(this.state, nextState);
}
render() {
return <div>{this.props.value}</div>;
}
}
const MemoizedComponent = React.memo(function MyComponent(props) {
return <div>{props.value}</div>;
}, (prevProps, nextProps) => {
return prevProps.value === nextProps.value;
});
|
不可变数据结构的优势
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
import { produce } from 'immer';
function reducer(state, action) {
return produce(state, draft => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'UPDATE_ITEM':
draft.items[action.index] = action.item;
break;
case 'ADD_ITEM':
draft.items.push(action.item);
break;
}
});
}
import { List } from 'immutable';
const list1 = List([1, 2, 3]);
const list2 = list1.push(4);
if (list1 !== list2) {
}
|
Diff算法的局限性
算法假设的局限性
- 相同类型的组件:假设产生相似的树结构
- Key的稳定性:假设key在整个生命周期中稳定不变
- 同级比较:无法处理跨层级的移动
边缘情况处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
function validateKeys(children) {
const keys = {};
React.Children.forEach(children, (child, index) => {
if (child.key != null) {
if (keys[child.key]) {
console.error(
'Duplicate keys detected: ' + child.key +
'. This can cause performance issues in React.'
);
}
keys[child.key] = true;
}
});
}
function generateStableKey(item, index) {
if (item.id) return item.id;
if (item.name) return item.name;
return `index-${index}`;
}
|
实战:实现简易Diff算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| class SimpleDiff {
static diff(oldChildren, newChildren) {
const patches = [];
const oldMap = this.createKeyMap(oldChildren);
let newIndex = 0;
let lastPlacedIndex = 0;
while (newIndex < newChildren.length) {
const newChild = newChildren[newIndex];
const oldIndex = oldMap[newChild.key];
if (oldIndex === undefined) {
patches.push({
type: 'INSERT',
node: newChild,
index: newIndex
});
} else {
const oldChild = oldChildren[oldIndex];
if (!this.isSameNode(oldChild, newChild)) {
patches.push({
type: 'UPDATE',
oldNode: oldChild,
newNode: newChild,
index: newIndex
});
}
if (oldIndex < lastPlacedIndex) {
patches.push({
type: 'MOVE',
from: oldIndex,
to: newIndex
});
}
lastPlacedIndex = Math.max(oldIndex, lastPlacedIndex);
delete oldMap[newChild.key];
}
newIndex++;
}
Object.values(oldMap).forEach(oldIndex => {
patches.push({
type: 'DELETE',
index: oldIndex
});
});
return patches;
}
static createKeyMap(children) {
const map = {};
children.forEach((child, index) => {
if (child.key != null) {
map[child.key] = index;
}
});
return map;
}
static isSameNode(a, b) {
return a.type === b.type && a.key === b.key;
}
}
|
React 18中的Diff改进
并发模式下的Diff
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| function reconcileChildrenConcurrent(
current,
workInProgress,
nextChildren,
renderLanes
) {
if (current === null) {
workInProgress.child = mountChildFibers(
workInProgress,
null,
nextChildren,
renderLanes
);
} else {
workInProgress.child = reconcileChildFibers(
workInProgress,
current.child,
nextChildren,
renderLanes
);
}
}
|
渐进式Hydration
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| function hydrateRoot(container, element) {
const root = createRoot(container, {
hydrate: true,
hydrationCallbacks: {
onHydrated: (suspenseInstance) => {
console.log('Component hydrated:', suspenseInstance);
},
onDeleted: (suspenseInstance) => {
console.log('Component deleted:', suspenseInstance);
}
}
});
root.render(element);
return root;
}
|
测试和调试
Diff算法的单元测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| describe('React Diff Algorithm', () => {
test('should handle element reordering', () => {
const oldChildren = [
{ key: 'a', type: 'div' },
{ key: 'b', type: 'div' },
{ key: 'c', type: 'div' }
];
const newChildren = [
{ key: 'c', type: 'div' },
{ key: 'a', type: 'div' },
{ key: 'b', type: 'div' }
];
const patches = SimpleDiff.diff(oldChildren, newChildren);
expect(patches).toContainEqual({
type: 'MOVE',
from: 2,
to: 0
});
});
test('should detect element updates', () => {
const oldChildren = [{ key: 'a', type: 'div', props: { className: 'old' } }];
const newChildren = [{ key: 'a', type: 'div', props: { className: 'new' } }];
const patches = SimpleDiff.diff(oldChildren, newChildren);
expect(patches).toContainEqual({
type: 'UPDATE',
oldNode: expect.any(Object),
newNode: expect.any(Object),
index: 0
});
});
});
|
性能分析和调试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
function ExpensiveList() {
const items = useMemo(() =>
Array.from({ length: 1000 }, (_, i) => ({ id: i, value: Math.random() }))
, []);
return (
<div>
{items.map(item => (
<ExpensiveItem key={item.id} item={item} />
))}
</div>
);
}
whyDidYouRender(React, {
trackAllPureComponents: true,
trackHooks: true,
logOnDifferentValues: true
});
|
最佳实践总结
1. 键值策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<Item key={item.id} />
<Item key={index} />
<Item key={Math.random()} />
|
2. 组件设计
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
class OptimizedComponent extends React.PureComponent {
render() {
return <div>{this.props.value}</div>;
}
}
function OptimizedComponent({ items }) {
const memoizedItems = useMemo(() => items.map(processItem), [items]);
const handleClick = useCallback(() => {
}, []);
return <div onClick={handleClick}>{memoizedItems}</div>;
}
|
3. 数据结构优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
const newState = {
...state,
items: [...state.items, newItem]
};
|
结论
React的Diff算法通过巧妙的启发式规则和优化策略,成功将树比较的复杂度从O(n³)降低到O(n)。